Leadership & Strategic Management MN7185
Friday, 10 July 2020
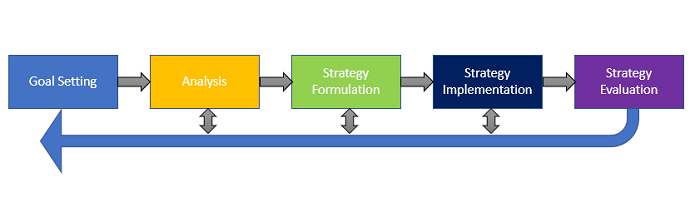
The 5 Stages of The Strategic Management Process

The 5 Stages of the Strategic Management Process
Strategic management
Strategic
management is the ongoing planning, monitoring, analysis, and assessment of all
necessities an organization needs to meet its goals and objectives. Changes in
business environments will require organizations to constantly assess their
strategies for success. The strategic management process helps organizations take
stock of their present situation, chalk out strategies, deploy them, and analyze
the effectiveness of the implemented management strategies. Strategic
management strategies consist of five basic strategies and can differ in
implementation depending on the surrounding environment. Strategic management
applies both to on-premise and mobile platforms. (SearchCIO, 2019)
5
Steps in the Strategic Management Process

1.
Goal setting
- ·
The purpose of goal-setting is to clarify
the vision for your business
- ·
Define both short- and long-term
objectives
- ·
Identify the process by which to
accomplish your objective
- ·
Give each person a task with which he can
succeed
Set a long-term organization-wide
strategic goal. This is the one goal all members of the organization should be
able to reproduce and chant at any time. The goal has to be emotionally
compelling but not just a daydream: it should be clear what success looks like.
2.
Analysis - Internal and external
- ·
Gather information and data relevant to
accomplishing your vision
- ·
Understand the needs of the business as a
sustainable entity
- ·
Examine any external or internal issues
that can affect your goals and objectives
When
the initial goals making up the strategic framework is agreed upon, it’s time
to assess your company’s capability to actually achieve the pursued goals.
Conduct a quick SWOT analysis for all goals you’ve set to take into account
internal and external factors.
3.
Strategy Formulation - Effort and Impact (and KPIs)
- ·
Determine what resources the business currently
has to reach the defined goals
- ·
Identify any areas for which the business
must seek external resources
- ·
Goals should be prioritized by their
importance to your success
4.
Strategy Implementation - Goals and Tasks
- ·
Be clear about everyone’s responsibilities
and duties, and how they fit in with the overall goal
- ·
Secure the resources needed to execute
tasks
Every
employee involved receives a set of responsibilities and tasks to be performed.
Every single task is connected to a goal. And performing every task as planned
should give you a decent shot at achieving the goal.
5.
Evaluation and Control
- ·
Determine your progress by measuring the
actual results versus the plan
- ·
If the strategy is not moving toward its
goal, take corrective actions
- ·
Any data gained in this stage should be
retained to help with any future strategies
(Boardview, 2016)
References
Boardview. (2016). The Five Stages of the Strategic
Management Process Boardview. [online] Available at:
https://boardview.io/blog/five-stages-strategic-management-process/.
Investopedia. (2019). Strategic Management.
[online] Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/strategic-management.asp.
SearchCIO. (2019). What is strategic management? -
Definition from WhatIs.com. [online] Available at: https://searchcio.techtarget.com/definition/strategic-management.
Zigu (2011). Strategic Management Process
Definition | Marketing Dictionary | MBA Skool-Study.Learn.Share. [online]
MBA Skool-Study.Learn.Share. Available at:
https://www.mbaskool.com/business-concepts/marketing-and-strategy-terms/7247-strategic-management-process.html.
Thursday, 9 July 2020
The Strategic Lenses
Strategic lenses
Different strategy lenses used to analyzes the Organization’s
strategic issues. Strategic lenses are a concept of strategic management. It is different ways of viewing strategy development. It examines the flow of tasks and information, or
how you get things done. Each lens reveals many different traits and qualities.
Using the strategic lens, one looks to optimize workflow
to meet the goals and objectives of the organization. This strategy can be
viewed and implemented on a corporate level; they are strategy as design,
experience, ideas, and discourse. (Francis, 2014)
1.
Strategy as a Design
This takes the view that strategy development can be a local
process in which the forces and constraints on the organization are weighted
carefully through analytic and evaluative techniques to establish a clear strategic
direction. This creates conditions in which carefully planned strategy
implementation should occur. They are
rationally, thoroughly researched, analytically considered strategies made by
experts.
It is a top-down approach to strategic decision making. It
takes no input from manager involved in the day to day operations. Strategic
decisions are imposed on them, they may resent this approach. It is suitable in a fast and rapidly changing environment where decision making is separate from
implementation.
2. Strategy as Experience
Here the view is that the future strategy of organizations are heavily
influenced by the experience of the managers and others in the organization
based on their previous strategies. Strategies are driven not so much by
clear-cut analysis as by the taken-for-granted assumptions and ways of doing
things embedded in the culture of organizations.
The experience lens views strategy development as the outcome of the individual and collective experience of people in organizations who influence
strategy or make strategic decisions and the
taken-for-granted assumptions.
In summary, the
experience lens provides a view of organizations as cultures within which
people make decisions about or influence strategy on the basis of their
cognitive (or mental) models and established ways of doing things (or
routines).
3. Strategy as Ideas
Neither of the above lenses is especially helpful in explaining innovation. Then how do ideas
come about? The idea lens emphasizes the importance of promoting diversity in
and around organizations, which can potentially generate genuinely new ideas.
It is an approach that requires innovation. These ideas can emerge from any level
or anywhere in the organization. It requires encouragement to employees to give
their views and suggestions and a mechanism to accommodate these ideas into a strategy.
It is suitable in an unpredictable macro-environment, where the ability to
respond to unforeseen situations is required. It can be used organization
developing new products or breaking into different markets. It can be used in
innovative industries where innovation is the key to success. E.g.
telecommunication industry and the fashion industry. It can also be used in newly
established business where owners as well as employees have little previous knowledge
and experience. They can benefit from the pooling of knowledge and experience.
4.
Strategy as
Discourse
This lens sees strategy in terms of language. Managers spend
most of their time communicating. Companies communicate their strategies by
presenting year reports, vision statements, or press releases. Managers and
shareholders debate about strategy when they discuss the future of the firm. We
can see strategies as stories, including a beginning (the present) and an end
(a successful future). Therefore command of strategy language becomes a resource
for managers by which to shape ‘objective’ strategic analysis to their personal
views and to gain influence, power, and legitimacy.
Reference
Altaf, U. (n.d.). The Four Lenses Strategic Framework
Toward an Integrated Social Enterprise Methodology. www.academia.edu.
[online] Available at:
https://www.academia.edu/9651202/The_Four_Lenses_Strategic_Framework_Toward_an_Integrated_Social_Enterprise_Methodology.
Francis, A. (2014). Strategic Lenses.
[online] MBA Knowledge Base. Available at:
https://www.mbaknol.com/strategic-management/strategic-lenses/ [Accessed 12 May
2020].
Saturday, 20 June 2020
Autocratic leadership and branch management
Autocratic leadership and branch
Application
of autocratic leadership
Introduction
Autocratic leadership is a management style wherein
one person controls all the decisions and takes very little inputs from other
group members. Autocratic leaders make choices or decisions based on their own
beliefs and do not involve others for their suggestions or advice. (https://economictimes.indiatimes.com)
Autocratic leaders impose their decisions, using their position to force people
to do as they are told. (Armstrong M, 309)
Autocratic leadership is a form of management
style in which one leader or member of the organization takes decisions on
behalf of the company. This type of leadership style is seen mostly in
businesses that are relatively small with fewer employees. This type of leadership style is
only effective in organizations where the nature of work requires quick
decision-making. The sole responsibility of the decision and the outcome is
with the leader.
Characteristics
of Autocratic Leadership
v The leader has all the
power and authority to make decisions on any topic.
v The leader assigns all
the task and delegates responsibilities to their group member without
consulting them.
v In this style of
leadership, leaders believe more in giving rewards and punishment rather
focusing on motivating employees.
v The leader takes all
responsibilities and credit for the accomplished task.
v The leader has no
confidence in their employee’s ability and closely supervises and controls
them.
Advantage
and Disadvantage
Here are some advantages and disadvantages to
the autocratic leadership style:
Advantages of Autocratic
leadership
v Effective when decisions must come quickly, without time to
consult others
v Prevents businesses or projects from becoming stagnant because
of poor organization or lack of leadership
v
Keeps individuals, groups or teams from missing important
deadlines
v
During stressful periods, autocratic leaders can be more
effective, and their teams appreciate their leadership
Disadvantages of Autocratic
leadership
v Invites potential
abuse by overly powerful personalities
v Can stifle staff and
discourage team creativity
v Modern employees may not
react well to authoritarian leadership
v Can discourage open
communication between leaders and subordinates
Exceptional leaders
adopt the style that fits their vision, behavior and personality. The
autocratic leadership style still works well in some institutions, such as the
military, manufacturing, restaurants and companies with aggressive sales
quotas.
This is more suitable
for bank branch when the majority of staff newly recruited. A leader who
centralizes authority, dictates work methods, makes unilateral decisions, and
limits employee participation. (Robbins et al, 2013)
Whether it’s an
athletic shoe company like Nike or a social media powerhouse like Facebook,
autocratic leadership is sometimes vital. Autocratic leaders help guarantee
deadlines are met by training people properly to assume responsibility for
their respective roles and to reach their goals.
At the end of the day,
autocratic leadership shares the same objectives as other styles. It’s all about
achieving success.
Where to use:
v This style of
leadership is used in an organization where strong centralized control is
required. For example in a Military organization.
v Organization in which
there is a fixed set of rules and structures.
v An extremely large
number of employees is to be handled.
v Organizations in which
employees are new, inexperienced, lack of qualification, and lack of skills.
When it is used:
v When quick decisions
are required.
v It is used during
emergencies and dangerous situations.
v It is used when the poor
performance of employees needs to be corrected.
Conclusion
Autocratic leadership is
one of the most traditionally relied upon models of leadership in the world.
This form of leadership places the decision-making within the hands of a
central figure, who rarely seeks input from others and attempts to make the
best decision for an organization out of his or her own expertise and
knowledge. This may be effective until the staff group with experience and
knowledge. This should be moved to the correct style with the expansion of the
branch and maturity of the staff. If not it can also be a leadership style that
discourages employee motivation in long term.
References
Armstrong, M., (2006). Hand Book of Human Recourse Management Practice. 10th ed.
[S.l.]: Kogen Page, pp.493-502.
Robbins,
S., DeCenzo, D., 2001. Fundamentals of Management Essential concepts and
applications. 3rd ed. India: Pearson Education, pp 343-371
Robbins,
S., DeCenzo, D. and Coulter, M., 2013. Fundamentals of Management Essential
concepts and applications. 8th ed. USA: Pearson, pp 302-303
Advantages and Disadvantages of Transformational Leadership
Advantages
and Disadvantages of Transformational Leadership
Introduction
The goal of any type of leadership is to get employees to perform beyond the
expected. While
transactional leaders do this by meting out rewards and punishments,
transformational leaders do this by influencing the values and attitudes of
others. It takes a special type of person to deliver an inspiring vision of the
future, and there are pros and cons associated with this leadership style.
Transformational
leadership
The
transformational leaders are effective because of several reasons such as the
leaders may be charismatic in terms of inspiring the employees, the
transformational leaders may meet the emotional need of the employees or they
may stimulate the employees intellectually (Bass & Avolio, 1994).
The personalized relationship developed by a transformational leader develops an
environment in which the employees feel happy and hence, their overall
performance is improved. Hence, it can be said that transformational leadership
and organizational performance are positively associated and transformational leadership has a significant impact on the performance of the
organization. (Jyoti and Dev, 2015)
The
idealized and behavioral charisma of the transformational leaders motivates the
followers to identify with the leader. (Jyoti and Dev, 2015)
Advantages
and Disadvantages of Transformational Leadership
·
Transformational leadership lowers
turnover costs.
·
It is a leadership style which engages the
full person.
·
Transformational leaders create and manage
change.
·
New corporate visions can be quickly
formulated.
·
It encourages ongoing learning and
development.
·
Transformational leaders are excellent
communicators.
·
It quickly changes low-morale situations.
·
Transformational leaders understand
relationships.
·
It is a leadership style which focuses
heavily on ethics.
·
Transformational leaders ask the important
questions.
·
This leadership style takes pride in the
outcomes achieved.
·
Transformational leaders seek to avoid
coercion.
·
People are treated as individuals.
1
Disadvantages
of Transformational Leadership
·
Transformational leaders can develop
negative outcomes.
·
There must be continual communication
available.
·
It requires constant and consistent
feedback.
·
Transformational leaders need their
followers to agree with them.
·
Risks are taken through transformational
leadership can be disruptive.
·
It can lead to employee burnout.
·
Transformational leaders often focus on
individual needs.
·
It is a leadership style that can focus on
deception.
·
Transformational leaders are not always
detail-oriented.
·
It is a leadership style which may ignore
certain protocols.
(Gaille, 2018)
The
Famous Transformational Leaders
Companies
founded by transformational leaders include Apple, IBM, Intel, and Microsoft.
Steve Jobs, Bill Gates and other hardware and software company leaders have
transformed not only the computer industry but the way other businesses work as
well.
Transformational
leaders in finance include business magnate Warren Buffett, Peter Lynch of
Fidelity and John Bogle of Vanguard. By offering people a vast array of
different ways to invest their money, these leaders have transformed the
financial industry. These leaders recognized the market for low-cost ways to
invest, such as mutual funds. Additionally, they've created opportunities to
bank and trade online. (Your
Business, n.d.)
Transformational
leadership and ABC bank
The
Bank’s well-spared network of branches places it in a unique position to
support the unbanked segments of the market through lending and deposits products.
Branch managers and relationship managers maintain relationships with the
society directly. Their management style directly affected the service level
and it will attract customers and increased business volume and profitability.
The bank consists of over six hundred branches all over the country and most
transformational leaders are a success as managers and perform well with the
corporation of subordinates.
Conclusion
Transformational
leadership enhances the motivation, morale, and performance of followers through
a variety of mechanisms. These include connecting the follower's sense of identity
and self to the mission and the collective identity of the organization; being
a role model for followers that inspires them; challenging followers to take
greater ownership for their work, and understanding the strengths and weaknesses
of followers, so the leader can align followers with tasks that optimize their
performance.
References
Annual
Report ABC Bank 2018
Bass,
B.M.; Avolio, B.J. Improving Organizational Effectiveness through
Transformational Leadership; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA,
1994.
Chron.com. (2019). Advantages and Disadvantages of
Transformational Leadership. [online] Available at: https://smallbusiness.chron.com/advantages-disadvantages-transformational-leadership-20979.html.
Gaille, B. (2018). 22 Advantages and Disadvantages
of Transformational Leadership. [online] BrandonGaille.com. Available at:
https://brandongaille.com/22-advantages-and-disadvantages-of-transformational-leadership/.
Jyoti, J., and Dev, M.
(2015). The impact of transformational leadership on employee creativity: the
role of learning orientation. Journal of Asia Business Studies,
[online] 9(1), pp.78–98. Available at:
https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/emerald-publishing/the-impact-of-transformational-leadership-on-employee-creativity-the-04uFNGE5He
[Accessed 15 Dec. 2019].
Your Business. (n.d.). Authoritative Leadership
Styles. [online] Available at:
https://yourbusiness.azcentral.com/authoritative-leadership-styles-16647.html.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)





